Everything you need to know about European hemp
Mostly grown for its seeds, fiber, or core (part of the stem), today hemp is opening up to new textile applications. Learn about the secrets of European hemp, from its agriculture background and history to new developments.
The different classifications of hemp
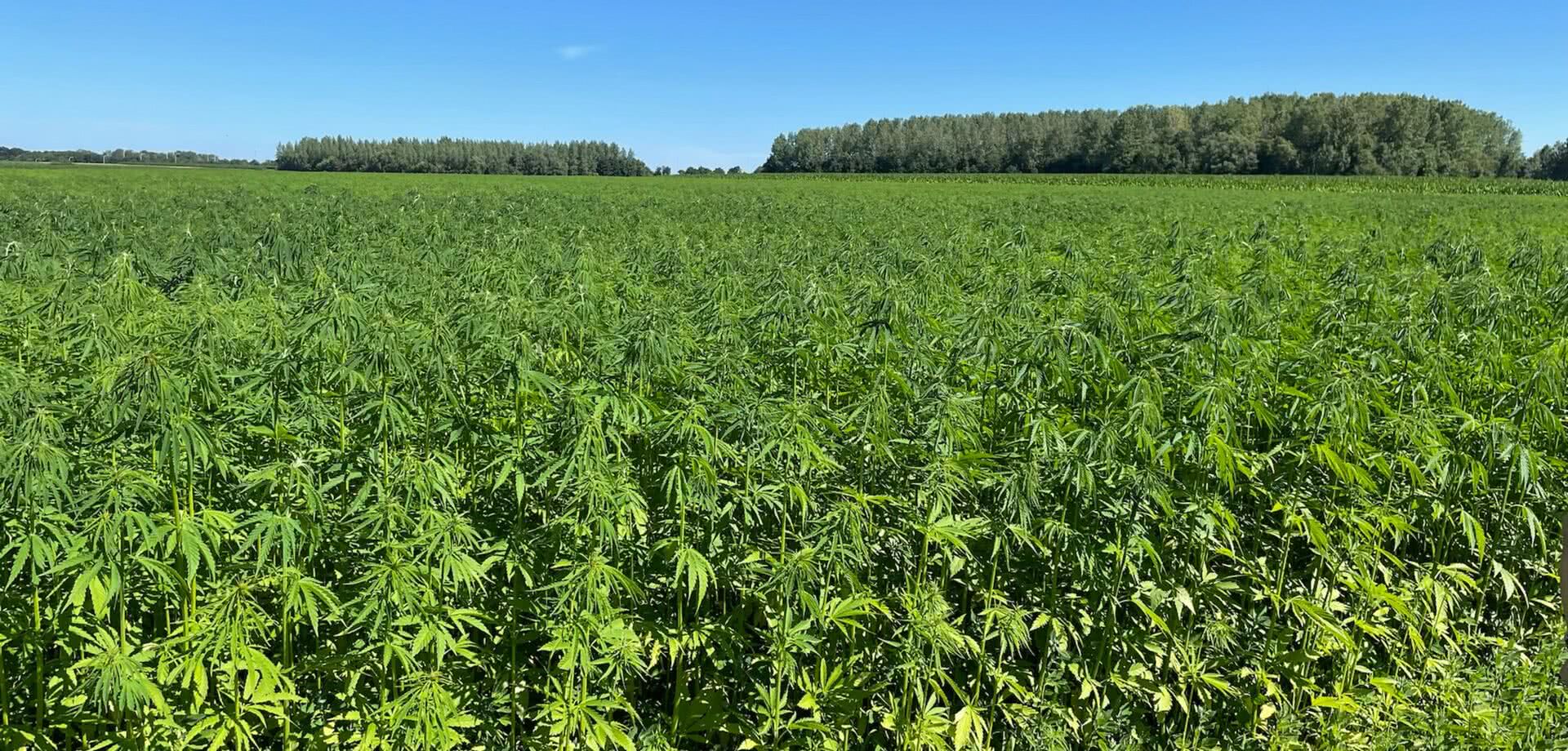
Hemp is grown in Europe, the world's second largest producer (France number 1), after China. Its bast fibers are used in paper products or the textile industry, and its core is prized in building construction. A superfood, its seeds are also popular as an ingredient beauty products.
sativa
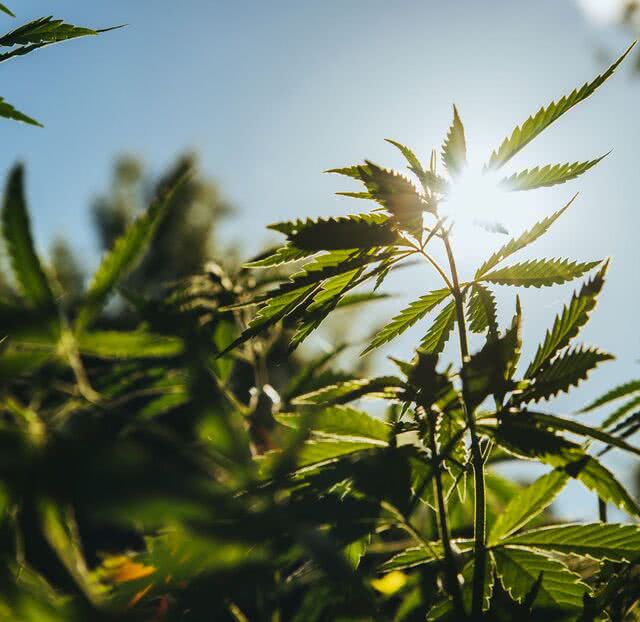


Cannabis sativa
Also known as hemp or cultivated hemp, Cannabis Sativa is an herbaceous perennial plant of the Cannabinaceae family, which also includes hops. Originating in Asia, it is one of the earliest domesticated plants in the world. It is characterized by large stems, leaves separated into long, toothed leaflets, and very rapid growth: plants reach maturity within three months on average. In the bast fiber family, hemp contains over 75% cellulose and 10-12% lignin (compared with 60% and 30% respectively for wood). Selected for its low THC* content (<0.3%), Cannabis sativa is the species grown in Europe for industrial hemp.
The Alliance and Cannabis sativa, a multifaceted industry showing rapid growth
Currently, the Alliance for European Flax-linen & Hemp is working on organizing the hemp sector, which has often directed its growth towards non-textile segments, in order to develop an additional offer of plant fiber. Historically, the Alliance has focused mainly on the technical applications (e.g., composites) of the natural fibers of Cannabis sativa.
A highly framed European culture
Hemp is subject to drastic French and European regulations (harmonized since 2004). These only allow varieties in the European Union that contain less than 0.3% THC. Seeds used for cultivation must therefore be certified and listed in the European catalogue. Each bag of seeds thus bears an official label from the SOC (official control service). Each year, in August, the THC level is checked in 30% of cultivated areas via samples sent to the laboratory.

Cannabis indica
Also known as Indian hemp or marijuana, Cannabis indica is a subspecies of Cannabis sativa. Originally from the Himalayas, it is a shorter plant with wider leaves, and an even shorter flowering phase (45-65 days). It is also different from sativa because of higher THC* content, placing it outside regulatory framework. In France, its cultivation and “recreational” use are illegal.
*THC : tetrahydrocannabinol, a psychoactive substance.
Hemp, a plant with many uses
From the seed (hempseed) to the stalk (core) by way of the fiber and flower, everything in the hemp plant has its use! It is no wonder that this Swiss knife of plants is so popular in food, cosmetics, textiles, paper products, and construction.
Hempseed


Hempseed
This is the name given to the seeds produced by hemp. Known for its exceptional nutritional qualities, this superfood is consumed at the table in the form of whole or shelled seeds, flour, oil, or food items (hemp does not contain any known allergens). The cosmetics industry is also interested in hemp oil for its hydrating properties. As for aviaries and fisheries, they are also large consumers of hempseed: it is a favorite food of birds and fish alike!
fibre
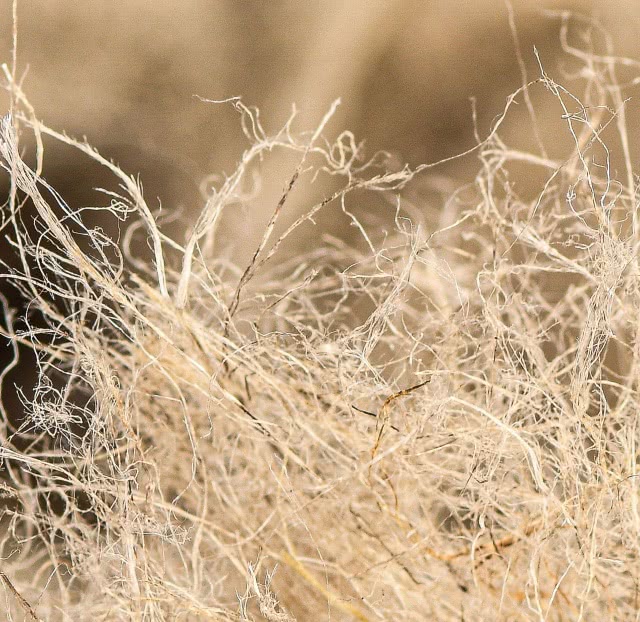


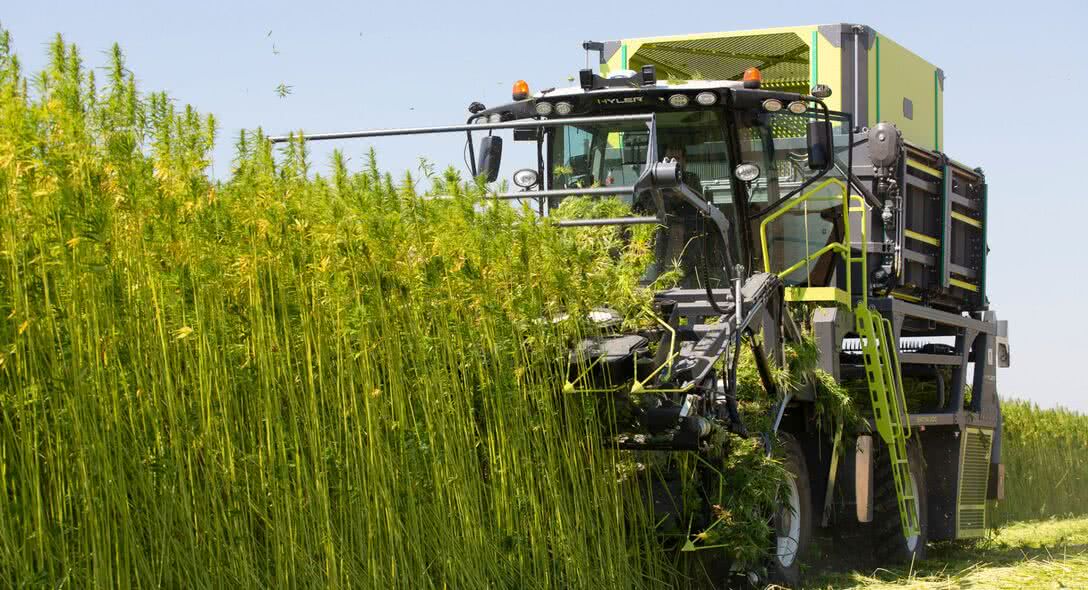
The fibre
For centuries, it has traditionally been used in ropemaking and to produce special paper, but also in textiles, in which it is currently experiencing a resurgence. Hemp fiber is also used in insulating wool and composite materials, such as bio-based plastics.
core
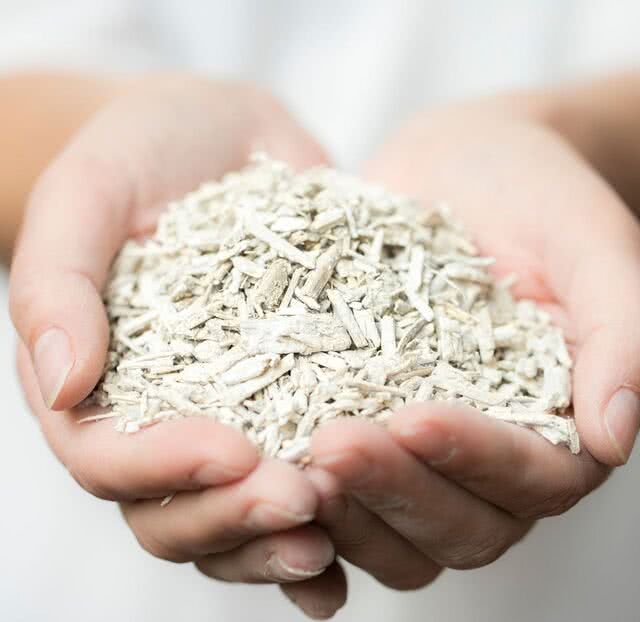


The core
This is the central part of the stalk, the woody part of the plant. It is used as garden straw and in animal litter. It is also becoming increasingly popular in construction (lightweight particle boards, hempcrete, etc.) thanks to its ability to insulate, as well as its temperature and energy performance.
powder

Organic powder
This powder (or dust), which occurs during decortication, is made up of fiber particles, the core, or mineral substances. It is normally used as a source of (green) energy, especially in compressed form as granules or bricks, but also as compost in the manufacture of compost.
flower
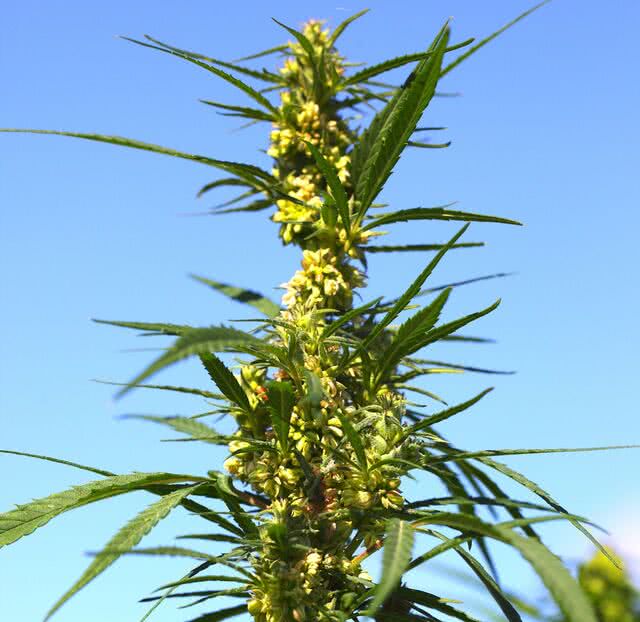


Flower
Since December 29, 2022, the Council of State has allowed the sale of flowers and raw hemp leaves with maximum THC content of 0.3%. This cannabidiol has no psychoactive effects and is mostly used as a pain reliever for medicinal purposes and to improve well-being.
The environmental properties of hemp
source : Terres Inovia Institut Agricole
Hemp, an ancestral fiber
Ever since the Neolithic, humans have used this rustic, beneficial plant to advance civilization. A journey through the history of hemp takes us to the earliest paper and medicinal texts, sea exploration, and the green revolution.
{{message}}